Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Yusuke*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2023-003, 67 Pages, 2024/02
A long-term geosphere stability for geological disposal is evaluated by the past geological environmental changes and modern conditions. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios ( D,
D, 
 O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for
O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for  D and
D and 
 O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of
O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of  D and
D and 
 O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the
O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the  D and
D and 
 O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
Saito, Takumi*; Nishi, Shusaku*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 3(12), p.4103 - 4112, 2023/12
Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Abe, Jun*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Polymer Journal, 55(11), p.1165 - 1170, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.7(Polymer Science)Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(46), p.32371 - 32380, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Although scientific knowledge of photolysis and radiolysis of water is widely used in the life sciences and other fields, the formation mechanism of the spatial distribution of hydrated electrons (spur) resulting from energy deposition to water is still not well understood. The chemical reaction times of hydrated electrons, OH radicals, and H O
O in the spur strongly depend on the spur radius. In our previous study, we elucidated the mechanism at a specific given energy (12.4 eV) by first-principles calculations. In the present study, we performed first-principles calculations of the spur radius at the deposition energies of 11-19 eV. The calculated spur radius is 3-10 nm, which is consistent with the experimental prediction (~4 nm) for the energy range of 8-12.4 eV, and the spur radius gradually increases with increasing energy. The spur radius is a new scientific knowledge and is expected to be widely used for estimating radiation DNA damage.
in the spur strongly depend on the spur radius. In our previous study, we elucidated the mechanism at a specific given energy (12.4 eV) by first-principles calculations. In the present study, we performed first-principles calculations of the spur radius at the deposition energies of 11-19 eV. The calculated spur radius is 3-10 nm, which is consistent with the experimental prediction (~4 nm) for the energy range of 8-12.4 eV, and the spur radius gradually increases with increasing energy. The spur radius is a new scientific knowledge and is expected to be widely used for estimating radiation DNA damage.
Terasawa, Tomoo; Matsunaga, Kazuya*; Hayashi, Naoki*; Ito, Takahiro*; Tanaka, Shinichiro*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito
Vacuum and Surface Science, 66(9), p.525 - 530, 2023/09
As Au (001) surfaces exhibit a quasi-one-dimensional corrugated structure, Hex-Au(001), its periodicity was predicted to change the electronic structure of graphene when graphene was grown on this surface. Furthermore, the hybridization between graphene and Au is known to introduce bandgap and spin polarization into graphene. Here, we report angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and density functional theory calculation of graphene on a Hex-Au(001) surface. A bandgap of 0.2 eV in the graphene Dirac cone was observed at the crossing point of the graphene Dirac cone and Au 6sp bands, indicating that the origin of the bandgap formation was the hybridization between the graphene Dirac cone and Au 6sp band. We discussed the hybridization mechanism and anticipated spin injection into the graphene Dirac cone.
Liu, H.*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Lei, J.*; Ren, Z.*
Physical Review C, 108(1), p.014617_1 - 014617_8, 2023/07
In this paper, we study deuteron-induced inclusive breakup reaction and explore the 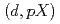 and
and 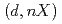 reactions for light and medium mass nuclei. Using the models of Ichimura, Austern, and Vincent and Glauber, we scrutinize the double differential cross-section of nonelastic breakup and compare the results for various reaction systems. Our findings indicate that the Glauber model, combined with a quantum
reactions for light and medium mass nuclei. Using the models of Ichimura, Austern, and Vincent and Glauber, we scrutinize the double differential cross-section of nonelastic breakup and compare the results for various reaction systems. Our findings indicate that the Glauber model, combined with a quantum  -matrix, produces remarkable results in the deuteron-induced inclusive breakup reaction. While both models are proficient in predicting the outcomes of light and medium mass nuclei, the
-matrix, produces remarkable results in the deuteron-induced inclusive breakup reaction. While both models are proficient in predicting the outcomes of light and medium mass nuclei, the 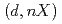 reaction showcases higher consistency than the
reaction showcases higher consistency than the 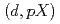 reaction. Nevertheless, there are still significant discrepancies between experimental and theoretical cross-sections that require further investigation and analysis. This study opens up a new realm of possibilities for future research in the field.
reaction. Nevertheless, there are still significant discrepancies between experimental and theoretical cross-sections that require further investigation and analysis. This study opens up a new realm of possibilities for future research in the field.
Kumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (115), p.43 - 49, 2023/04
Oxidation and dissolution of uranium oxide materials has been a subject of numerous studies as a basis of the geological disposal technology for spent nuclear fuel. The understandings obtained by these studies provide useful suggestions for research and development regarding the retrieval and storage of nuclear fuel debris generated by a nuclear severe accident. Here, these research backgrounds of oxidative dissolution of uranium oxides are briefly reviewed and some studies relating to radiation-induced reactions will be introduced.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Watanabe, Ritsuko*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 158(16), p.164103_1 - 164103_8, 2023/04
New insight into water radiolysis and photolysis is indispensable in the dramatic progress of sciences and technologies in various research areas. In the radiation field, reactive hydrated electrons are considerably produced along radiation tracks. Although the formation results from a transient dynamic correlation between ejected electrons and water, the individual mechanisms of electron thermalization, delocalization, and polarization are unknown. Using a dynamic Monte Carlo code, we show herein that the ejected electrons are immediately delocalized by molecular excitations in parallel with phonon polarization and gradually thermalized by momentum transfer with an orientation polarization in a simultaneous manner. Our results show that these mechanisms heavily depend on the intermolecular vibration and rotation modes peculiar to water. We expect our approach to be a powerful technique for connecting physical and chemical processes in various solvents.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tezuka, Tomoya*; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(11), p.7076 - 7086, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:81.33(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Scientific insights of water radiolysis are widely used in the life sciences and so on, however, the formation mechanism of radicals, a product of water radiolysis, is still not well understood. We are challenging to develop a simulation code to solve this formation mechanism from the viewpoint of radiation physics. Our first-principles calculations have revealed that the behavior of secondary electrons in water is governed not only by collisional effects but also by polarization effects. Furthermore, from the predicted ratio of ionization to electronic excitation, based on the spatial distribution of secondary electrons, we successfully reproduce the initial yield of hydrated electrons predicted in terms of radiation chemistry. The code provides us a reasonable spatiotemporal connection from radiation physics to radiation chemistry. Our findings are expected to provide newly scientific insights for understanding the earliest stages of water radiolysis.
 high energy resolution XAFS
high energy resolution XAFSYamamoto, Naoki*; Matsumura, Daiju; Hagihara, Yuto*; Tanaka, Kei*; Hasegawa, Yuta*; Ishii, Kenji*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
Journal of Power Sources, 557, p.232508_1 - 232508_10, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.01(Chemistry, Physical)Liu, S.*; Yang, D. S.*; Wang, S.*; Luan, H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Model, J. B.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Ghaffari, R.*; Rogers, J. A.*
EcoMat (Internet), 5(1), p.e12270_1 - e12270_18, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:91.64(Chemistry, Physical)Advanced capabilities in noninvasive, in situ monitoring of sweat serve as the basis for obtaining real-time insights into human physiological state, health, and performance. Although recently reported microfluidic systems support powerful functions, most are designed as single-use disposables. Here, we introduce materials and molding techniques that bypass these concerns through biodegradable microfluidic systems with a full range of features. The key components fully degrade through the enzymatic action of microorganisms in natural soil environments. Detailed characterization of the device reveal a set of essential performance parameters that are comparable to, or even better than, those of non-degradable counterparts. Human subject studies illustrate the ability of these devices to acquire accurate measurements of sweat loss, sweat rate, pH, and chloride concentration.
Terasawa, Tomoo; Matsunaga, Kazuya*; Hayashi, Naoki*; Ito, Takahiro*; Tanaka, Shinichiro*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014002_1 - 014002_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Au(001) surfaces exhibit a complex reconstructed structure [Hex-Au(001)] comprising a hexagonal surface and square bulk lattices, yielding a quasi-one-dimensional corrugated surface. When graphene was grown on this surface, the periodicity of the corrugated surface was predicted to change the electronic structure of graphene, forming bandgaps and new Dirac points. Furthermore, the graphene-Au interface is promising for bandgap generation and spin injection due to band hybridization. Here, we report the angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and density functional calculation of graphene on a Hex-Au(001) surface. The crossing point of the original and replica graphene  bands showed no bandgap, suggesting that the one-dimensional potential was too small to modify the electronic structure. A bandgap of 0.2 eV was observed at the crossing point of the graphene
bands showed no bandgap, suggesting that the one-dimensional potential was too small to modify the electronic structure. A bandgap of 0.2 eV was observed at the crossing point of the graphene  and Au
and Au 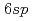 bands, indicating that the bandgap is generated using hybridization of the graphene
bands, indicating that the bandgap is generated using hybridization of the graphene  and Au
and Au 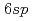 bands. We discussed the hybridization mechanism and concluded that the R30 configuration between graphene and Au and an isolated electronic structure of Au are essential for effective hybridization between graphene and Au. We anticipate that hybridization between graphene
bands. We discussed the hybridization mechanism and concluded that the R30 configuration between graphene and Au and an isolated electronic structure of Au are essential for effective hybridization between graphene and Au. We anticipate that hybridization between graphene  and Au
and Au 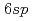 would result in spin injection into graphene.
would result in spin injection into graphene.
 -edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
-edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
Yomogida, Takumi; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Kumagai, Yuta; Higashi, Kotaro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kirishima, Akira*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(50), p.20206 - 20210, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)FeUO was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L
was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L -edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
-edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
 O
O solution
solutionKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.961 - 971, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)We investigated potential degradation of fuel debris caused by H O
O , which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H
, which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H O
O solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H
solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H O
O . Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H
. Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H O
O reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO
reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO improves the stability of fuel debris against H
improves the stability of fuel debris against H O
O reaction.
reaction.
Iwasa, Toma; Arima, Tatsumi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-036, 23 Pages, 2022/03
Knowledge on the liquefaction (thermal decomposition and melting) temperatures of MA-bearing nitride fuels for transmutation by accelerator-driven system is essential for elucidation of the fuel behaviors under abnormal condition and for the safety analysis. A melting temperature measurement system for refractory materials was developed based on a laser spot heating method, which is expected to measure in a very short time with a small amount of sample, and demonstration tests using refractory metals and zirconium nitride were performed. As the results, it was found that this melting temperature measurement system can be applicable up to the temperatures around 3000 K which is close to the thermal decomposition temperature of nitride fuels and we confirmed the technical feasibility of this system for future application to small specimens of transuranium nitrides.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Few-Body Systems, 63(1), p.4_1 - 4_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for not only science and engineering fields but also medical applications. For the engineering design of such facilities, accurate and comprehensive nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions are indispensable. However, it is difficult to meet the requirement by employing experimental data alone. Thus, theoretical model calculations play a key role in completing the necessary nuclear data by interpolation and extrapolation of experimental data. Under the above situations, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In the present work, calculations using DEURACS are compared with available experimental data and validation of the present modelling in DEURACS is discussed. Moreover, the importance of consideration of the breakup processes for accurate prediction of deuteron-induced reactions is also presented.
 mesocrystal formation
mesocrystal formationLi, Z.*; Piankova, D.*; Yang, Y.*; Kumagai, Yuta; Zschiesche, H.*; Jonsson, M.*; Tarakina, N. V.*; Soroka, I. L.*
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 61(6), p.e202112204_1 - e202112204_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.82(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The role of intermediate phases in CeO mesocrystal formation from aqueous Ce(III) solutions subjected to
mesocrystal formation from aqueous Ce(III) solutions subjected to  -radiation was studied. Radiolytically formed hydroxyl radicals convert soluble Ce(III) into less soluble Ce(IV). Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction studies of samples from different stages of the process allowed the identification of several stages in CeO
-radiation was studied. Radiolytically formed hydroxyl radicals convert soluble Ce(III) into less soluble Ce(IV). Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction studies of samples from different stages of the process allowed the identification of several stages in CeO mesocrystal evolution following the oxidation to Ce(IV): (1) formation of hydrated Ce(IV)-hydroxides, serving as intermediates in the liquid-to-solid phase transformation; (2) CeO
mesocrystal evolution following the oxidation to Ce(IV): (1) formation of hydrated Ce(IV)-hydroxides, serving as intermediates in the liquid-to-solid phase transformation; (2) CeO primary particle growth inside the intermediate phase; (3) alignment of the primary particles into "pre-mesocrystals" and subsequently to mesocrystals, guided by confinement of the amorphous intermediate phase and accompanied by the formation of mineral bridges. Further alignment of the obtained mesocrystals into supracrystals occurs upon slow drying, making it possible to form complex hierarchical architectures.
primary particle growth inside the intermediate phase; (3) alignment of the primary particles into "pre-mesocrystals" and subsequently to mesocrystals, guided by confinement of the amorphous intermediate phase and accompanied by the formation of mineral bridges. Further alignment of the obtained mesocrystals into supracrystals occurs upon slow drying, making it possible to form complex hierarchical architectures.
Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 191, p.109831_1 - 109831_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, we investigated and compared the effects of a high-silica zeolite (HMOR) on the radiation-induced degradation of three aromatic chlorides, 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh), 2-chloroaniline (2-ClAn), and 2-chlorobenzoic acid (2-ClBA), in order to examine its potential to reduce the influence of ions in water matrix in the irradiation treatment of water-soluble organic compounds. In the presence of ions reactive to radicals, the degradation of 2-ClPh in water was inhibited, but the combined use of HMOR much improved the degradation yield. This improvement was attributed to high performance of HMOR in adsorption of 2-ClPh. Similarly, HMOR was effective for adsorption of 2-ClAn and facilitated the 2-ClAn degradation by irradiation. In contrast, HMOR was poor at adsorption of 2-ClBA and consistently the degradation of 2-ClBA in the water-HMOR mixture was inhibited by the radical scavenger. These results demonstrate that HMOR can mitigate the influence of radical scavengers in water.
Hata, Kuniki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.468 - 473, 2021/12
In order to estimate corrosive environment in the contaminated water at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, effects of oxidants, such as H O
O , which were generated from water radiolysis, should be taken into account due to the irradiation field in the reactor building. The process of water radiolysis and the amounts of these oxidants can change depending on the conditions of water and types of radiation. After the accident, a variety of factors, which can affect water radiolysis, such as seawater constituents, surface of oxides, and
, which were generated from water radiolysis, should be taken into account due to the irradiation field in the reactor building. The process of water radiolysis and the amounts of these oxidants can change depending on the conditions of water and types of radiation. After the accident, a variety of factors, which can affect water radiolysis, such as seawater constituents, surface of oxides, and  -radionuclides, had been discussed. In this paper, these effects on radiolysis are reviewed for the better understanding of the corrosive environment in the contaminated water.
-radionuclides, had been discussed. In this paper, these effects on radiolysis are reviewed for the better understanding of the corrosive environment in the contaminated water.
 Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O :Ce single-crystal scintillator to neutron radiography
:Ce single-crystal scintillator to neutron radiographyIsegawa, Kazuhisa; Setoyama, Daigo*; Kimura, Hidehiko*; Shinohara, Takenao
Journal of Imaging (Internet), 7(11), p.232_1 - 232_9, 2021/11
Neutron radiography is regarded as complementary to X-ray radiography in terms of transmittance through materials, but its spatial resolution is still insufficient. In order to achieve higher resolution in neutron imaging, several approaches have been adopted such as optical magnification and event centroiding, and the authors focused on modification of the scintillator in this paper. A Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O :Ce single-crystal scintillator was applied to neutron radiography for the first time and was achieved a spatial resolution of 10.5 micrometers. The results indicate that this material can be a powerful candidate for a new neutron scintillator providing a resolution in micrometer order by optimizing the optical system and increasing the scintillator luminosity.
:Ce single-crystal scintillator was applied to neutron radiography for the first time and was achieved a spatial resolution of 10.5 micrometers. The results indicate that this material can be a powerful candidate for a new neutron scintillator providing a resolution in micrometer order by optimizing the optical system and increasing the scintillator luminosity.